
Modern customers want to engage with automotive brands digitally, and the brands are sparing no effort to boost their presence by growing their digital spending. Customers expect services at the drop of a hat. From AI assistants to virtual showrooms, the brands are giving it all. However, a growing digital footprint also increases security risks. How can they protect it with security solutions to ensure the least number of disruptions?
The rate of digital transformation has gone remarkably high in the past few years. The market for cloud computing in 2010 stood at USD 24 Billion. By 2020, it reached USD 156.4 Billion, growing by about 645% in a decade. In 2028, the market will surpass USD 1 Trillion as most enterprises will depend on cloud technology.1
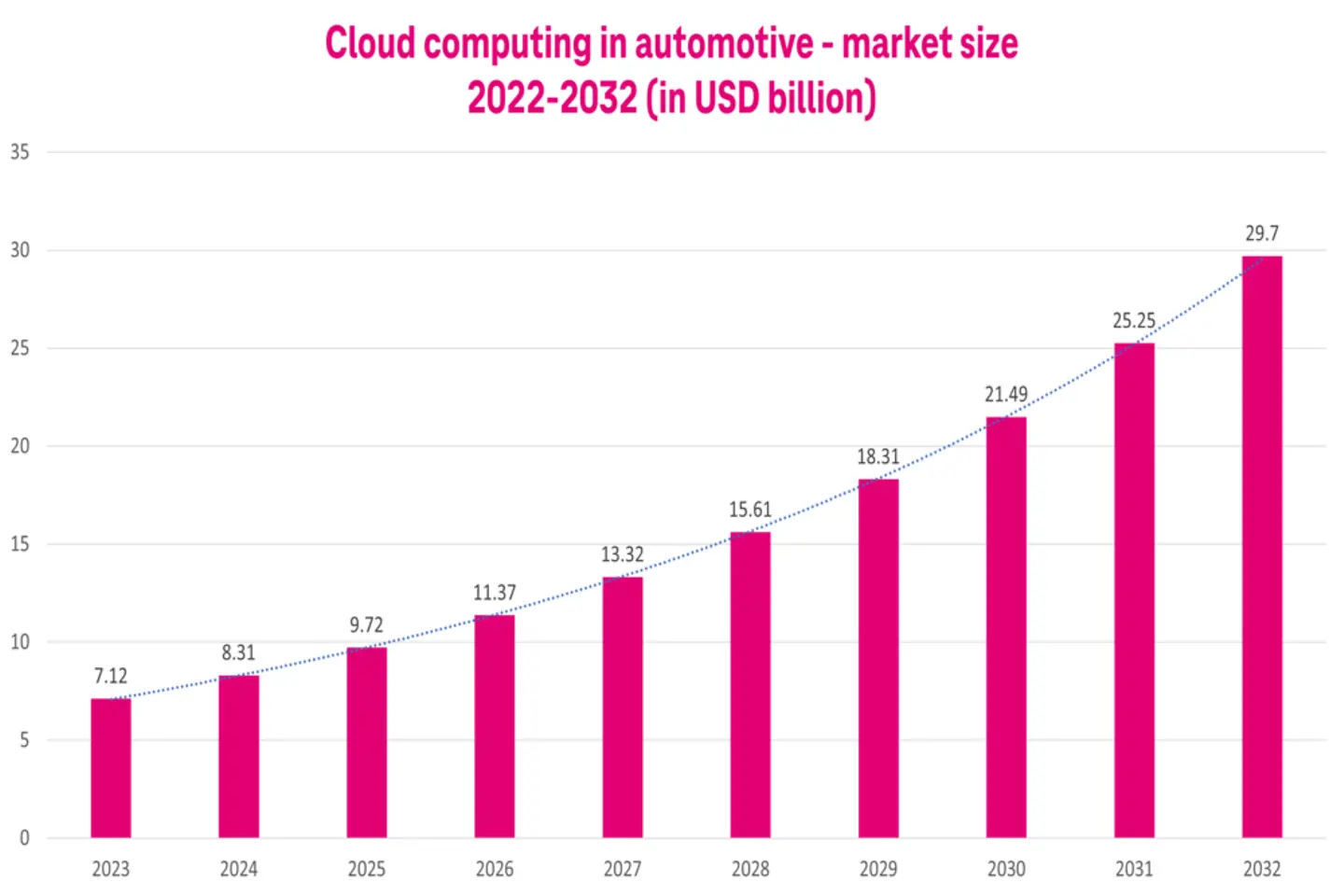
The automotive industry is also adopting digital technologies. For example, cloud computing in the automotive industry is growing at a CAGR of 17.2%. By 2030, the market will reach USD 21.49 Billion.2
Automotive brands use these technologies to offer better services, bring efficiency to operations, and provide a range of benefits to customers. While driving experience and build quality are table stakes in the automotive industry today, customer experience is the X factor that gives brands the competitive edge. Customers want a seamless, connected, and personalized experience across multiple channels, from better shopping to after-sales experience. They are no longer in the passenger seat.
No matter where customers buy from, whether in the store or online, 87% of them start product searches online.3 To enable better discovery, automotive OEMs are heavily increasing their online presence. More than 60% of buyers under 45 are likely to buy their next cars online.4 Such trends indicate a strong customer preference for digital interactions. This compels brands to rethink customer touchpoints and create an omnichannel customer experience.
Rising customer expectations: Customers want a faster and simpler experience. They want to discover the brands easily online, compare, research, and engage through different channels such as websites, mobile applications, social media, and more. They are willing to abandon a brand if they have a bad experience. About 86% of customers leave a brand if they have two or more encounters of poor experience. 49% of the customers have left a brand that they have been loyal to.5 Around 80% of automotive customers are ready to change brands, dealerships, or service providers for a better experience.6
Changing consumer behavior: Customers no longer rely on traditional methods of enquiries and purchase from a physical store or dealership only. They are increasingly becoming digital-first and are more aware of brands, benchmarks, features, prices, and more.
Competitive edge: An engaging omnichannel customer journey allows brands to stand out in a highly competitive market. Brands that offer a consistent experience are likely to retain customers and increase loyalty.
Enhanced customer engagement: Through interactive websites, immersive virtual showrooms, personalized mobile apps, and social media platforms, brands can engage customers and build stronger relationships. Brands with strong online presence also come across as transparent.
Data-driven insights: Brands can also collect valuable data and generate insights about customer preferences, behavior, and purchase patterns across different channels. Analyzing this data can help them understand their customer preferences better. Customer intelligence enables brands to create personalized strategies.
A customer’s omnichannel journey begins from the research and discovery stage and continues until post-purchase. Within this journey, brands use applications and digital touchpoints to keep the customer engaged and offer the right information. For instance, brands make discoverability easier by having a website presence and facilitating customers to browse through product information, features, pricing, etc., making it easier for them to compare the product against other brands.

Some automotive OEMs even have virtual showrooms. For instance, Mercedes-Benz offers a virtual showroom facility for its prospects to interact with its vehicle models in an immersive environment. Prospects can open the doors, sit inside, and check infotainment features in this virtual showroom, which can be accessed online through VR headsets.
Going further, the company has built Augmented Reality (AR)-enabled apps that allow users to scan a QR code and watch videos or even visualize a car in their surroundings. Mercedes-Benz also uses AR to improve the after-sales experience. Customers can receive service-related notifications on the dashboard screens or get navigation-related assistance, etc.
Automotive brands realize that customer experience is the central piece to business growth, and they are leaving no stone unturned. They have ramped up their digital presence. It is estimated that about 6 million vehicles will be sold online by 2025. The online car-buying market will scale further. In 2020, the market was valued at USD 237 Billion, whereas in 2030, it’ll reach about USD 722 Billion – growing at a CAGR of about 12%.7
For example, automotive company Tesla, has shifted its marketing and sales strategy online since 2019. In 2019, Tesla’s revenues stood at USD 24.5 Billion and went up to USD 96.7 Billion in 2023.8 Tesla disrupted the market with its direct-to-consumer sales strategy where customers can buy an Electric Vehicle (EV) in under 10 clicks. Digital customer experience with consistency and personalization underpins Tesla’s online strategy.
Brands such as BMW have been in the market for more than a century and have thousands of dealerships and showrooms. However, they too are concentrating on growing their online and digital presence. BMW aims to sell about 25% of its cars online by 2025.9 It has already adopted data management platforms to offer personalized and unified customer experience across channels. Numerous other brands have started following suit. About 70% of automotive brands now offer an online sales experience.10
Good customer experience can rake in online sales and revenues. Automotive OEMs must realize that customer experience doesn’t end at online sales — they must further invest in after-sales processes. Transforming after-sales not only ensures consistency, but can also unlock newer revenue opportunities.
For example, there are paywalled features that automotives provide. Tesla offers autopilot features that customers can unlock by paying additional fees. Mercedes offers a rear-wheel-steering feature, that allows extra steering. BMW offers heated seat features that can be accessed with a subscription. Some automotive OEMs sell ‘battery-as-a-service’ through mobile applications.
With digital technology, companies can take customer experience up by notches through innovation. Features are released periodically to further augment the experience. Brands leverage over-the-air (OTA) updates, entertainment packages, aftermarket services, and so on to trigger new revenue streams. Revenues can go up by as much as 30% with these recurring services alone.11
To unlock revenue-making services and enable a rich customer experience, automotive OEMs are already partnering up a lot more with software companies. That shift is already happening, the automotive software and electronics market is expected to reach a staggering USD 462 Billion by 2030.12
To that end, let’s find out which applications and technologies are being used to engage the customer at different digital touchpoints:
All these solutions are run by different technologies. For example, data analytics is used to process vast amounts of data captured during various stages of the customer journey. Analytics generate insights and trends that help brands make changes in product features, enable preventive maintenance, extend marketing outreach, and improve customer support.
Analytics tools help brands to get insights from customer data. With these insights, they can create targeted marketing campaigns to ensure that customers receive relevant offers and information, thereby enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
For instance, the Volkswagen Group Sweden has invested in a customer experience management (CEM) platform to improve customer satisfaction levels. The analytics platform helps the brand to take a customer-driven approach across all touchpoints and also empowers dealers to offer better services.15
On top of analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can help automotive brands to predict customer behavior and embrace market changes better. AI-based sales assistants are also used by brands such as Mercedes-Benz. The German automaker plans to use AI to improve website functionalities, assist in customer support, and help browse products by offering intuitive experiences.16
Virtual showrooms are underpinned by Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies to create immersive experiences. Cloud services are used to host applications and to ensure real-time delivery and service availability. Cloud services enable scalable infrastructure for websites, e-commerce platforms, CRMs, and other applications.
Web and mobile technologies are integral parts of omnichannel customer experience as key applications are built to offer seamless experiences to users at their fingertips. Mobile apps are used right from the discovery phase to service management, appointment scheduling, real-time updates, and so on.
A significant touchpoint in the customer journey is also the in-car experience. This experience is offered through connected cars and infotainment features. This could include digital touchscreen displays, navigational control, real-time traffic and weather updates, remote vehicle management, advanced driving assistant systems (ADAS), voice assistants, wireless connectivity, etc. There are also other comfort features such as heated seats, ambient lighting, advanced sound systems, and more. Such in-car experience is enabled through user interfaces, mobile applications, voice control, IoT, AI, cloud computing, 5G connectivity, sensors, etc.
Modern vehicles release new features through OTA updates. OTA updates enhance the in-car experience by allowing manufacturers to remotely update the vehicle’s software, improve functionality, add new features, and fix bugs without requiring a visit to the dealership.
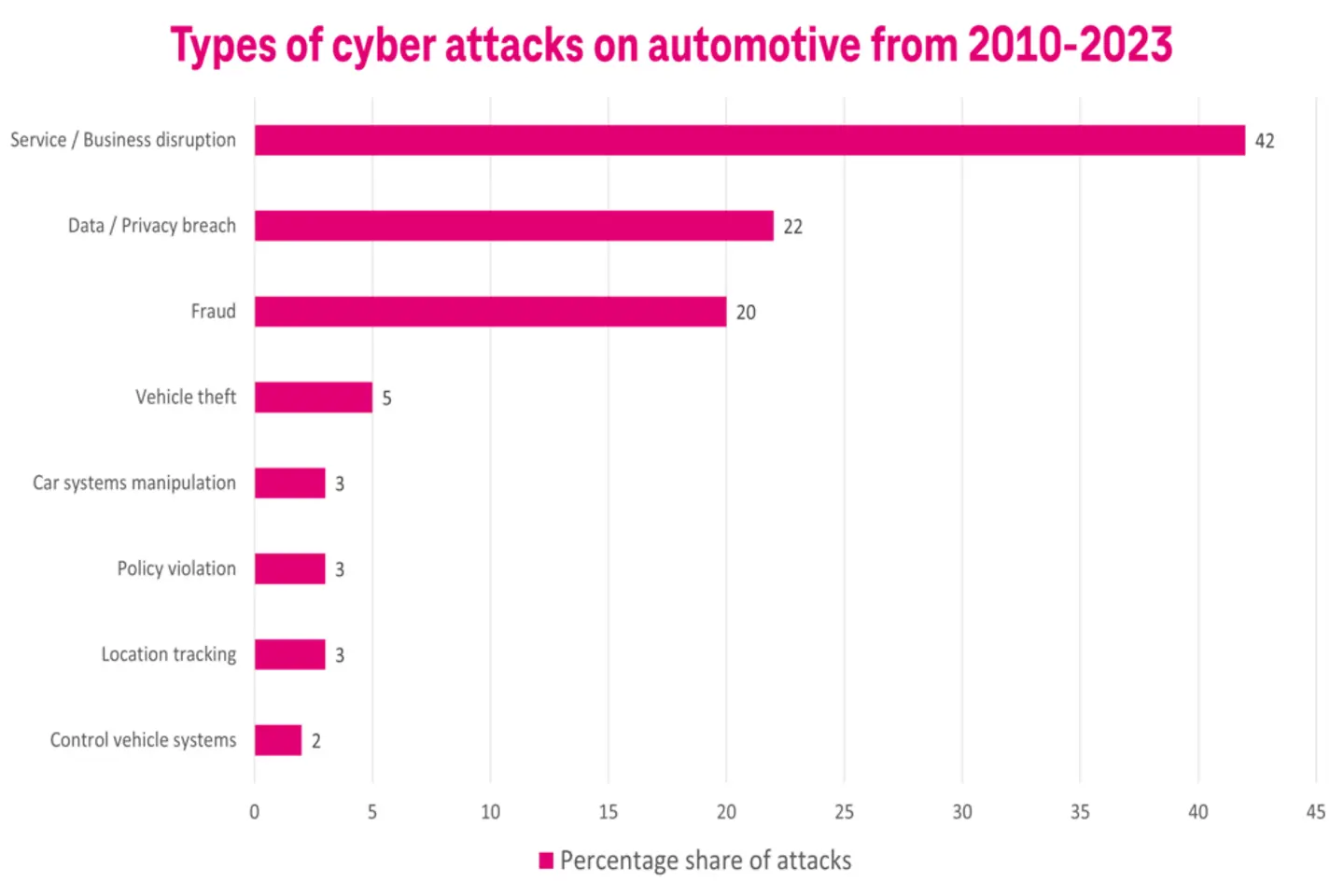
As the usage of more technology and applications grows in the automotive industry, the digital attack surface also expands. Cyber security incidents have been rising, owing to newer attack methods and increased threats. The losses owing to attacks are also going up globally; by 2025, the attacks will lead to damages worth USD 10.5 Trillion.17
Cyber attacks disrupt daily business operations and the availability of customer-facing services and applications. Business disruption directly impacts customer experience due to service unavailability and downtime.
For instance, a DDoS attack can make website service unavailable by flooding the website with internet traffic and overwhelming the server resources. Customers trying to browse information or book a test ride on the website may not be able to access these website features, leading to a bad customer experience.18
This is just one example, there are many other instances where customer touchpoints can become unavailable or compromised due to a security incident. Such experiences can turn the customer away from the brand.
In 2023, Japanese automaker Toyota faced a cyber attack that leaked data of about 2 million customers.19 This data breach was a result of cloud misconfiguration. In another incident, Toyota Financial Services faced a ransomware attack. Cyber attackers were able to get hold of customer data such as full names, contact information, bank account numbers, lease-purchase details, etc. Medusa gang was said to be behind this attack.20
Modern customers understand a secure, reliable, and seamless experience today. Customers are also concerned about how their data is being handled, stored, and used. They don’t want to engage with a brand that they don’t trust to handle their data. This makes it imperative for automotive players to integrate cyber security as a part of their customer experience strategy. Furthermore, strong cyber security also improves compliance rates, building trust with stakeholders.
Data encryption: Data breaches can be avoided using strong data encryption methods. Applications such as CRM can be secured by encrypting sensitive customer data and ensuring that only authorized users have access to it. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS): SSL & TLS can be used to ensure that communication between servers and browsers is safer. These security measures avoid man-in-the-middle attacks.
Penetration testing: All applications need to be tested for vulnerabilities. White box, black box, and gray box methods can help organizations uncover weaknesses in the system, and get them fixed before attackers exploit them. For instance, in 2022, a bug was discovered by researchers in the mobile application of Hyundai, the South Korean automotive giant. This bug led to giving unauthorized access to users. The users could gain remote access and control of the car.21 This incident emphasizes the importance of having applications tested for vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can help monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and alert the security teams for a real-time response. Here is a security incident faced by Australia’s largest automotive dealer: Eagers Automotive faced an attack that led to service downtime at some of its locations, leading to delivery issues. Customers impacted by the breach were notified by the dealer. The company had to swallow the bitter pill and offer an apology to customers. Since the company uses several applications even today to offer customer services, they rejigged security measures to protect customer data and cloud environments from further intrusions.22
Identity Access Management (IAM): Applications can be protected with an IAM security solution to manage user identities and control access, ensuring that only authorized users can view and sign documents, and protect against unauthorized access. IAM can also protect digital documentation and contract signing solutions.
Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Unauthorized access to applications can be avoided by using an MFA security solution. It acts as an additional security layer. It requires users to verify their identity through multiple factors, such as a password plus a one-time code sent to their phone or email. This brings down the risk of unauthorized access even if the password has been stolen or leaked.
Cloud security: With applications and customer data stored in the cloud, securing the database becomes important. Cloud security measures ensure that the data stored in the cloud is protected from unauthorized access, breaches, and other security threats. This includes using encryption for data at rest and in transit, access control mechanisms, and regular security audits. Security measures such as redundancy, disaster recovery plans, and regular backups are also integral to cloud security.
Network security monitoring: Network security monitoring continuously monitors the network traffic to detect and respond to potential security threats, ensuring the integrity and security of networked systems.
In-car security or software-defined vehicle security is also significant because attacks originating from infotainment systems, device-related attacks, keyless car theft, etc. have increased manifold. Such attacks also disrupt the customer experience. This blog covers software-defined vehicle security in detail.
Instead of buying too many point security products, automotive OEMs can contemplate buying solutions that have these features bundled together. T-Systems can help you with comprehensive security solutions.
Managed Detection and Response (MDR): The MDR solution has endpoint detection, protection & response capabilities. On top of these capabilities, it can also include IDS and Security Operations Center (SOC) to make security highly effective.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): SASE consolidates security services such as SSL, Secure Web Gateways (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), API Gateways, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Firewall as a Service (FWaaS) to offer secure access to applications. SASE enforces the least privilege and zero trust principles to grant access to users who should have access.
We can also help you get started with initial assessment and security consulting services. For more details, get in touch with us.
1. Cloud Cost Playbook, 2023, Cloud Zero
2. Global Cloud Computing in Automotive, 2023, Precedence Research
3. Press Release, 2024, Fox2 Now
4. Digitization in Automotive, 2021, McKinsey & Company
5. Customer Experience Article, 2022, Business Wire
6. Customer Experience in Automotive, 2020, Smoke
7. Online Car Buying Market, 2021, Allied Market Research
8. Tesla Revenues, 2024, Macrotrends
9. BMW vs Tesla Article, 2022, Forbes
10. Online Tesla Sales Article, 2023, Bearing Point
11. Key to Automotive Success, 2021, McKinsey & Company
12. Automotive Software & Electronics Market, 2023, McKinsey & Company
13. Automotive Social Media Marketing, 2023, Drift Rock
14. Ford Customer Experience Article, 2019, The Detroit News
15. Customer Satisfaction Article, 2023, AG Analytics
16. Mercedes AI Sales Assistant Article, 2024, CDO Magazine
17. Cybercrime Cost Report, 2020, Cybercrime Magazine
18. Cybercrime Impact in Automotive, 2024, Statista
19. Toyota Data Breach, 2023, Cyber Security Hub
20. Toyota Ransomware Attack, 2023, GB Hackers on Security
21. Hyundai App Bug Article, 2022, Cybernews
22. Eager Cyber Attack Article, 2023, Go Auto News