
Waiting for a cyber attack to expose vulnerabilities in your systems is akin to playing with fire. Organizations cannot risk taking that approach anymore. They can go on the offensive with penetration testing. In this blog, find out how penetration testing can serve an organization’s interest in ramping up security measures. How businesses can gain speed and scale with automated penetration testing, and anecdotes of companies that could have avoided costly data breaches.
As the attack surface grows and organizations are plagued with cyber attacks, the demand for penetration testing (also known as pen testing and ethical hacking) is undoubtedly growing. Penetration testing isn’t a new phenomenon. In 1967, about 15,000 security experts and other professionals gathered in a conference to discuss whether communication lines could be penetrated.1
In a way, this was the beginning of the penetration testing process – where security teams would orchestrate attacks on their infrastructure to find out security vulnerabilities in systems, networks, hardware, software, etc. Although the methodologies have advanced, the goal is to fill the security gaps and improve the security posture.
Organizations realize that many of these cyber attacks or data breaches are outcomes of attackers exploiting an existing vulnerability or more in the system. However, they only comprehend this in hindsight after an attack has already taken place. Naturally, pen testing is a good proactive approach to identify weaknesses in the system before any security incident or data breach.
Data breaches are becoming commonplace. In 2023, more than 8 billion records were breached in about 2,800 security incidents.2 Data breaches can cost organizations a lot of money. The average cost of a data breach stood at $4.45 million in 2023.3 Can data breaches be avoided with offensive security approaches such as penetration testing? By all means, yes.
Some of the common reasons for data breaches are weak and broken authentication, unpatched software, misconfigured services and applications, insecure APIs, etc. With penetration testing, these problems can be identified in advance. Issues such as weak authentication and broken access may seem insignificant, but they can cause catastrophic damage.
In 2019, First American Financial Corporation, a US-based finance services company, faced a data breach in which about 885 million sensitive documents were exposed.4 These documents were related to customers’ bank account numbers, statements, mortgage records, and so on.
All these documents were stored on the company’s website page and intended to be accessed by specific users. However, anyone who managed to get to the link of this webpage could get their hands on this sensitive customer data. This is a simple case of an authentication problem, which was exploited. In 2023, the company reached a $1 million settlement with the New York State Department of Financial Services (DFS).
Equifax, another US-based credit reporting agency, suffered a data breach in 2017 due to a web portal vulnerability, which cost them $1.4 billion in settlements. Read more about it here.
To cut to the chase, penetration testing tools could have detected security vulnerabilities early on and prevented the damaging outcomes.
Pen testing is usually carried out by the security team in a phased manner, as explained below:
Apart from identifying weaknesses, organizations conduct pen testing for several other reasons, such as to assess the effectiveness of the existing security controls, to meet compliance requirements, and to manage and mitigate cyber security risks. It builds confidence amongst stakeholders and customers.
Penetration testing is different from vulnerability assessment. Vulnerability assessment aims just to identify weaknesses in the systems, while penetration testing aims to exploit these weaknesses and gauge the impact of the attack and the effectiveness of the security controls.
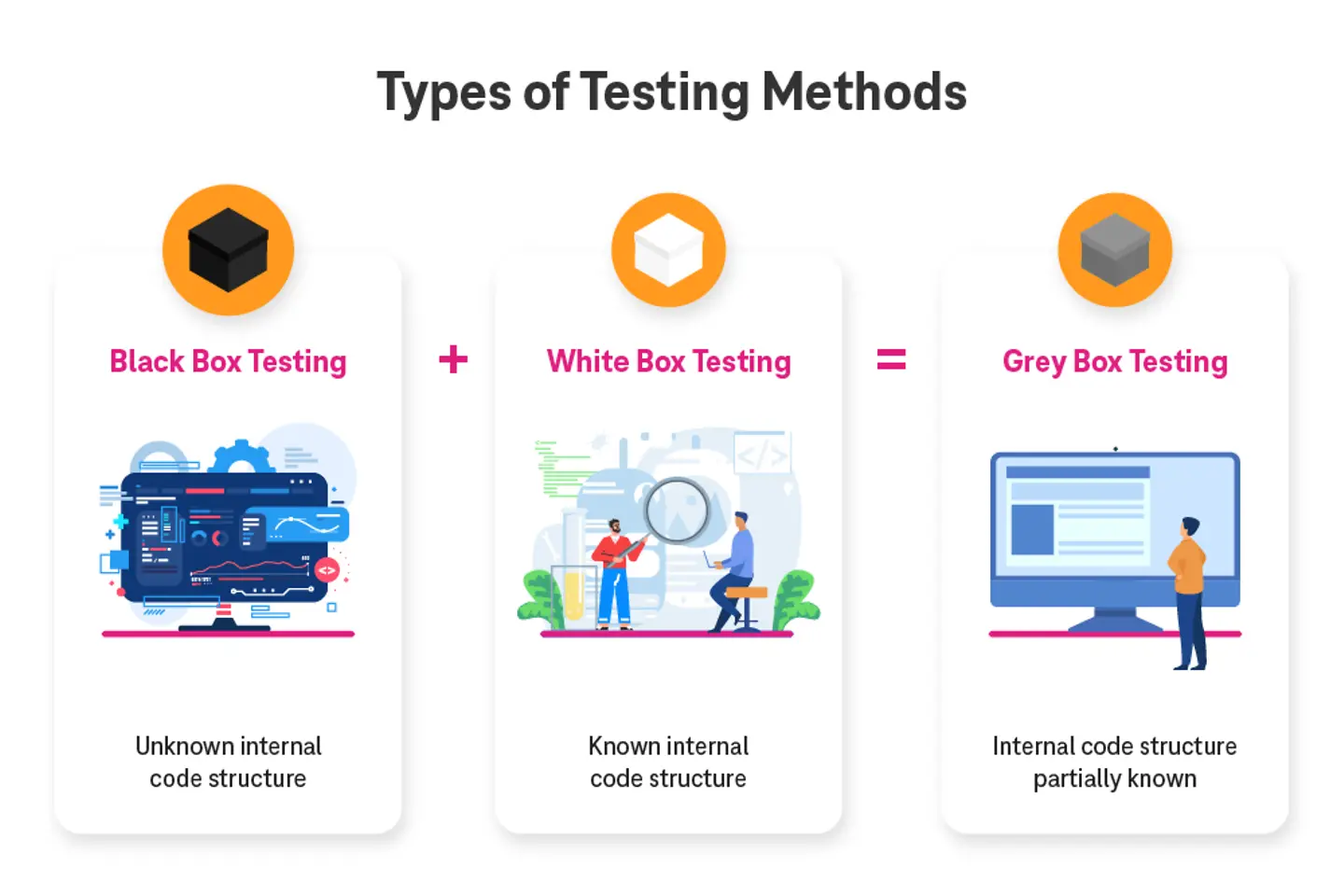
Pen testing is performed to assess different systems such as networks, web applications, APIs, wireless networks, social engineering (to check vulnerabilities in human behavior), physical penetration, red team (full-fledged real-world attack simulation), and so on.
These systems are tested by launching attacks both from outside and inside of the organization. Depending on what access and information is given to the penetration tester, there are three categories.
However, there are certain challenges with manual penetration testing.
These downsides of manual penetration testing encourage businesses to opt for automated penetration testing.

In the automated pen testing approach, organizations rely on the use of advanced tools rather than human intervention to identify vulnerabilities within the organization’s network, applications, or systems. Any business, regardless of scale, with a digital landscape and attack surface can use this automated approach to put up proactive cyber defense.
Automated pen testing makes a compelling case for its adoption. It streamlines the processes and allows faster execution of the testing process, cutting down the timeframe of the project. This is one of the key features, because repetitive and time-consuming tasks can be automated with the workflows. It can mimic an array of attack scenarios to speed up the testing process.
It also enables repeatability so that organizations can go through routine assessments. The ability to scan and monitor continuously allows organizations to discover new weaknesses, outdated/unpatched applications, misconfigurations, weak authentication, incorrect access controls, and so on. These can be fixed to ensure minimal disruptions and business continuity. Organizations can also gather insights through detailed analysis and reporting capabilities. The reports also generate a system risk profile by ranking vulnerabilities according to their severity.
Organizations can deploy automated penetration testing across large infrastructures without worrying about scalability and coverage issues. This testing approach is also a cost-effective alternative because businesses don’t need to invest a lot of time and money in hiring skilled security testers.
While automated penetration testing doesn’t eliminate the need for human intervention altogether, the efforts needed is lesser, allowing security teams to focus on other critical functions.
Reconnaissance: Automated tools gather information about the target network, systems, applications, entry points, and vulnerabilities.
Scanning: Scanners are systematically deployed to probe the target environment for open ports, services, and vulnerabilities.
Enumeration: Automated tools compute system details, such as user accounts, network shares, and configurations, to further refine the scope of potential exploits.
Exploitation: Scripts are deployed to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access, execute commands, and manipulate system resources, mimicking real-world attack scenarios.
Post-exploitation: Continuation of gathering information, escalating privileges, and maintaining access to compromised systems.
Reporting: Detailed report generation of findings from the automated pen testing. This report also includes severity, recommendations for remediation, and prioritization.
All these phases are carried out with the help of automated tools. These tools offer a framework for developing, testing, and executing exploits against the target systems. Some of these tools also have a vast database of known vulnerabilities, making automated pen testing very effective. They can detect weaknesses in SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), server misconfigurations, etc.
Some of the popular tools for automated penetration testing in the market are RidgeBot, Metasploit, Nessus, OpenVas, Burp Suite, Armitage, Nmap, SQL Map, ZAP, and more.
Businesses are shifting towards automated pen testing to proactively identify vulnerabilities in their systems and mitigate the risks of cyber attacks and data breaches. They want to improve security posture, enhance compliance rates, and protect data with offensive security strategies. Damages such as financial and reputational losses and legal liabilities can be avoided through such security approaches.
With demonstrated experience and expertise, we can conduct comprehensive network and web application penetration testing. Post-testing, we offer a technical and executive report with our recommendations that help you prioritize the next steps. Our security experts are Offensive Security Certified Professionals (OSCP) and they adhere to best industry practices and regulatory frameworks. We also follow the MITRE ATT&CK framework for standardization, mapping, in-threat emulation, risk assessment, and continuous improvement.
Build confidence in offensive cyber security strategy with us. Begin a conversation with us to know more.
For detailed information, download the flyer.
1 The History Of Penetration Testing, 2019, Infosec Institute
2 List Of Data Breaches, 2024, IT Governance
3 Cost Of Data Breach, 2023, IBM
4 First American Financial Data Leak Article, 2019, Forbes
5 Broken Access Control Report, 2021, OWASP