
With over 200 services, AWS opens doors for innovation. But without proper configuration, there can be security vulnerabilities. So, it's crucial to secure and govern your public cloud environment. The AWS Security Hub and SHARR enable central access for security checks, alerts, and automated remediations for the entire AWS environment. Check out how to establish fundamental security management, even without a dedicated security team or a huge budget.

The AWS Security Hub is automatically enabled if you have an AWS Organization. New accounts added to your organization will appear automatically in the dashboard.
Because AWS Config rules contain most of the security checks differentiated in the various playbooks, it's good practice to enable AWS Config for your AWS Organization.
Once AWS Config is activated, it makes sense to delegate the Security Hub administration permissions to a dedicated security account according to AWS best practices. Your security account gives you an overview of the entire organization via the Security Hub dashboard.
If you do not have an AWS Organization, it's possible to activate the Security Hub manually.
At first glance, you will see the security score on the dashboard. It's expressed as a percentage from 0 to 100 and reflects the ratio of passed controls to activated controls.
All controls are treated equally for the security score; criticality is not a factor in calculating it. However, further down in the dashboard, you have the criticality of the findings sorted by region. The dashboard also has insights like "Accounts with the most findings (by resource type)" and many others. It's also possible to switch to other service integrations like Guard Duty, AWS Inspector, AWS Macie, and many others.
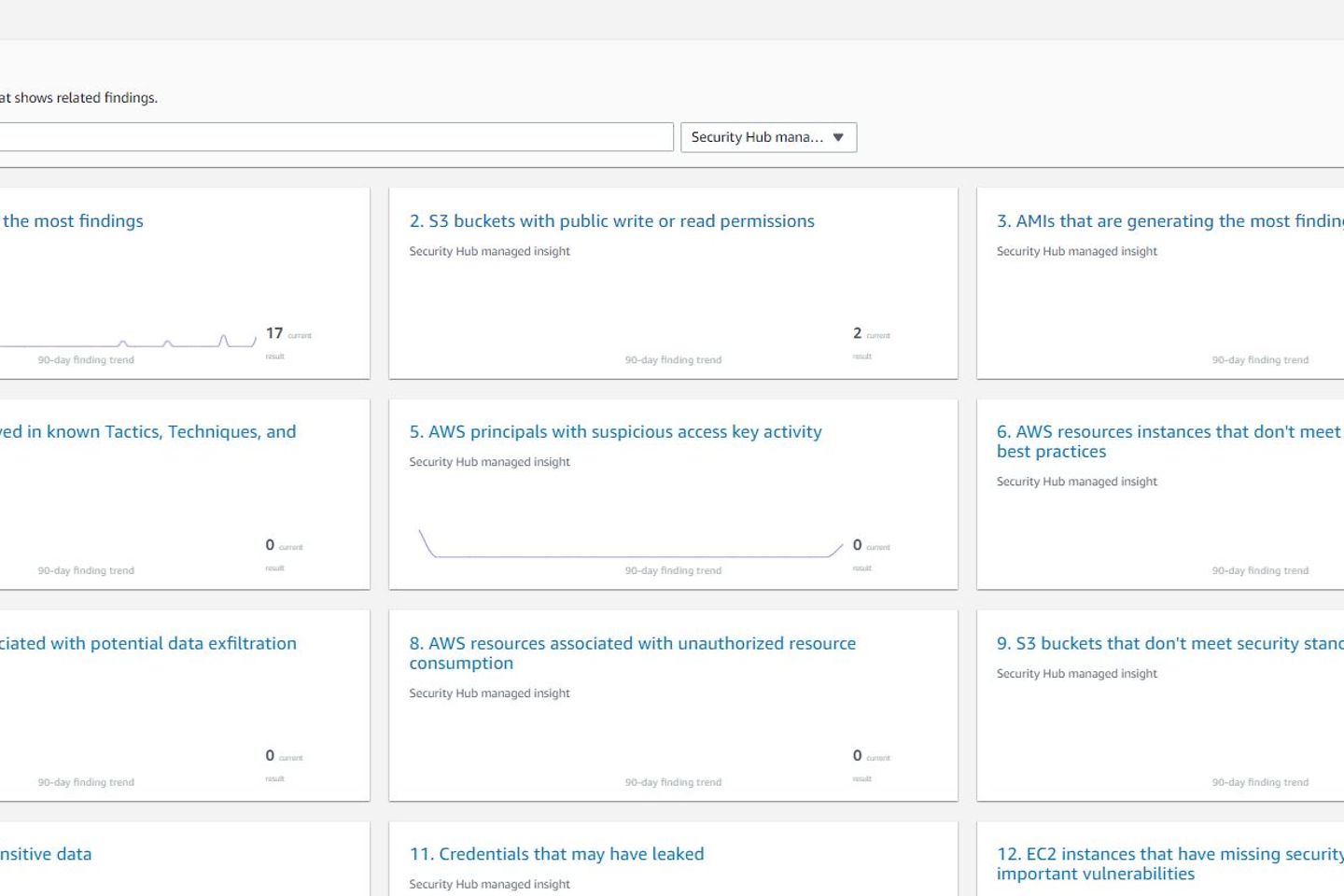
The Security Hub would only be half as interesting without the security standards. They contain controls to determine compliance based on AWS's security best practices.
The following AWS security standards are available and need to be enabled individually:
The Security Hub includes pre-configured insights used as filters for Findings. The insights help to find and prioritize the critical findings faster. It's also possible to set up your own so-called custom insights.
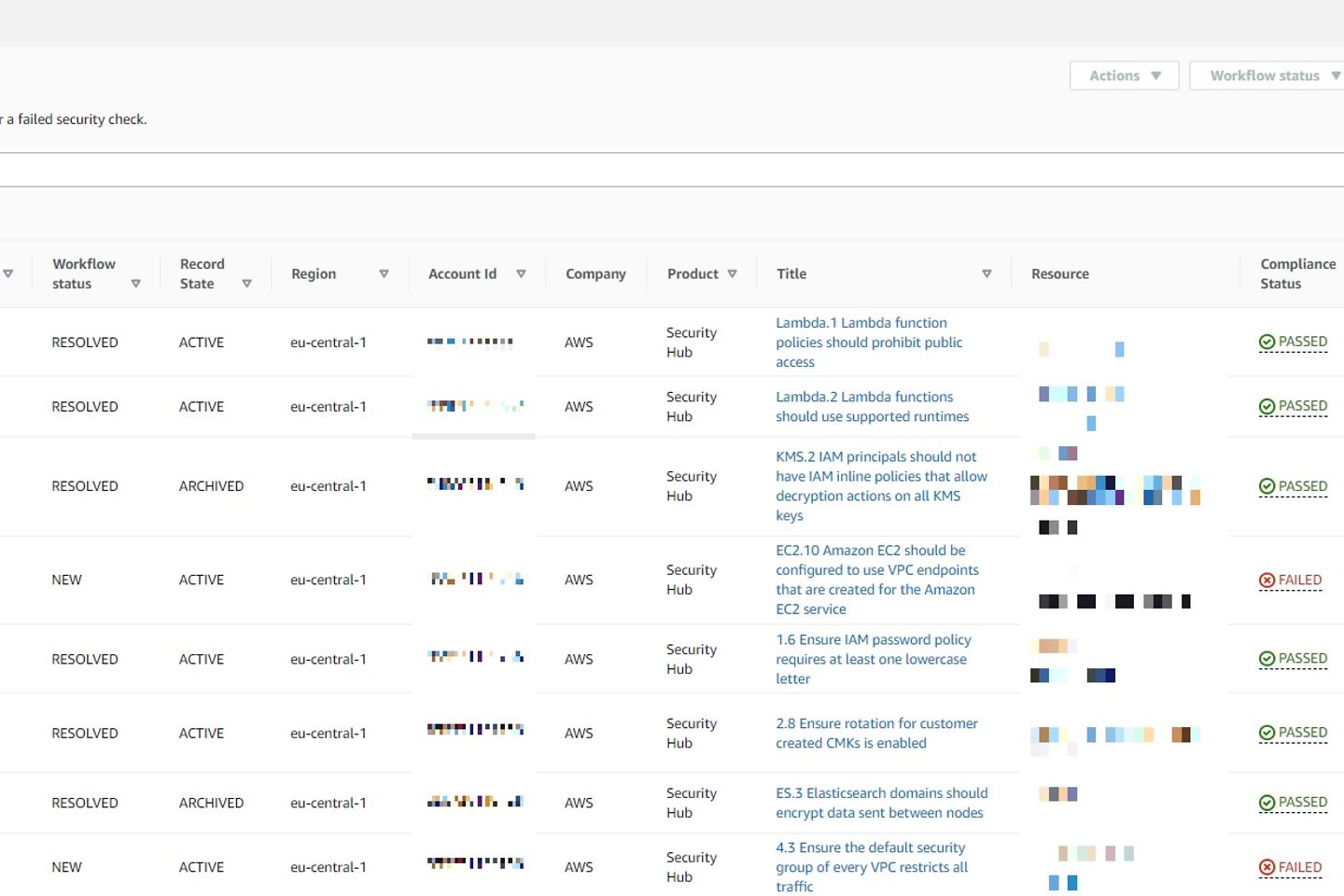
The findings in the Security Hub consist of the checks of the enabled security standards, AWS services (such as Amazon Inspector, Amazon GuardDuty, AWS Firewall Manager, etc.), third party integrations (e.g., Cloud Custodian), or custom integrations that are not available via the third-party integrations.
Several filtering and sorting options are available, including severity, product, or the currentness of the finding. In the central Security Hub account holding the Security Hub administration permissions for the AWS organization, you can also see the findings for the individual accounts.
If you have integrated the Security Hub Automated Response and Remediation (SHARR) solution, you can remediate the finding automatically by using the action button. It's also possible to adjust a finding's workflow status.
As mentioned, AWS Security Hub makes it possible to integrate other products. These can be AWS services like the Amazon Inspector and even third-party services like Cloud Custodian, to name one. The findings of these services are then visualized via the AWS Security Hub. The advantage of these integrations is that the Security Hub provides a central point of view for many other security and compliance tools/services.
SHARR stands for Security Hub Automated Response and Remediation. This solution is an add-on for the Security Hub service. There are a number of response and remediation actions that can be applied across your AWS Organization. These remediations are based on some of the controls of the security standards. You can choose the remediations to be performed automatically or manually via the Security Hub dashboard.
Usually, you will have built your own logic in your environment to respond to compliance or security violations automatically. The advantage of SHARR is that it is an official solution from AWS and therefore the available response and remediation actions are built according to AWS best practice and can be used immediately.
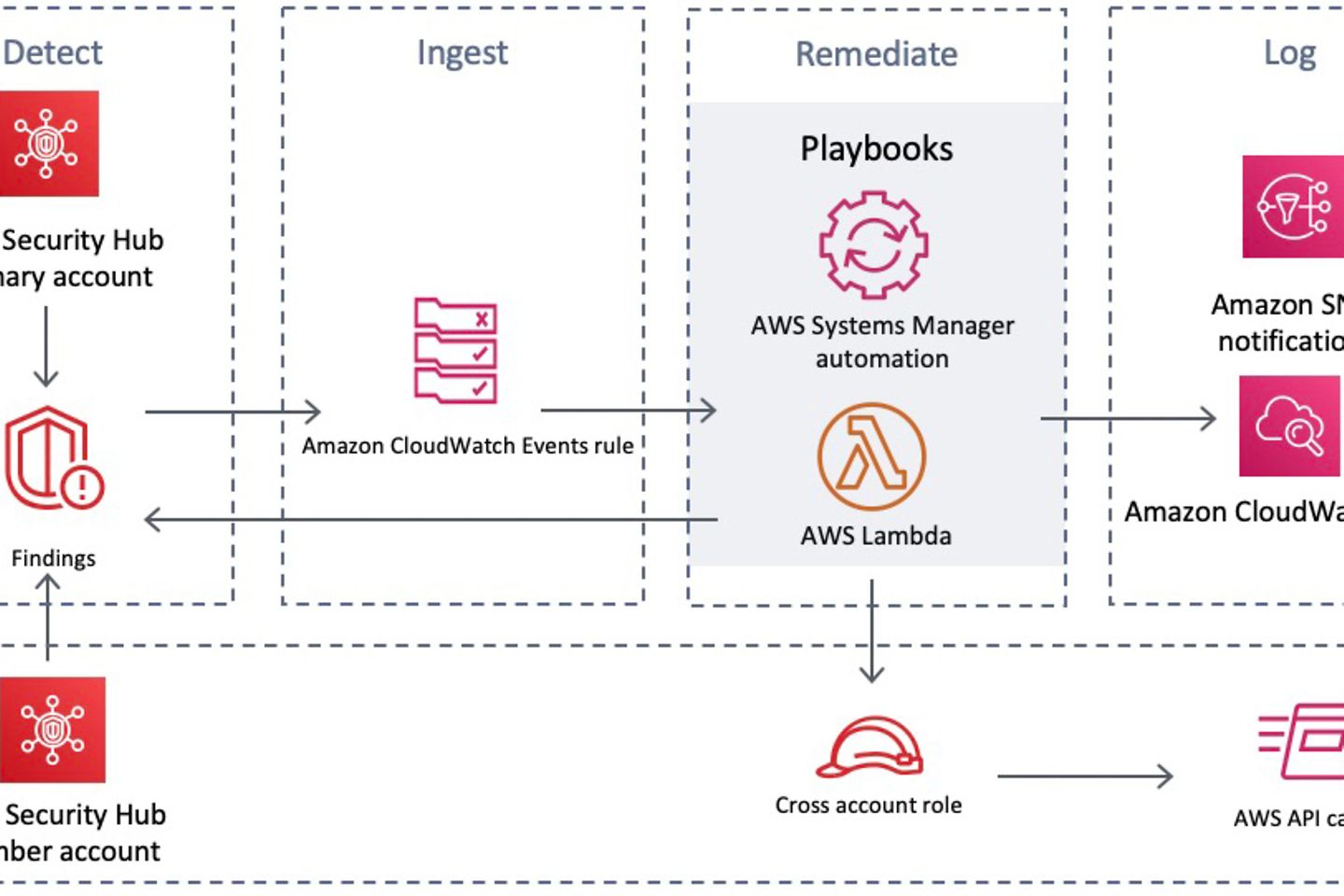
The solution adheres to the basic workflows detect, ingest, remediate, and log. For detection, the findings of the security standards are taken into account. The Amazon CloudWatch Event rules are used to trigger the respective playbooks that contain the remediations. These can be executed automatically or manually via AWS Security Hub Custom Actions. Subsequently, the playbooks use the stored logic partly via Lambda functions and partly via AWS Systems Manager automation documents to execute the respective remediation.
After execution, results are stored in a CloudWatch Log Group, a notification is sent to an Amazon SNS topic, and in addition, the Security Hub finding workflow status is updated. The workflow status of the finding is updated to NEW, NOTIFIED or RESOLVED and furthermore a finding note is stored describing what exactly has been done.
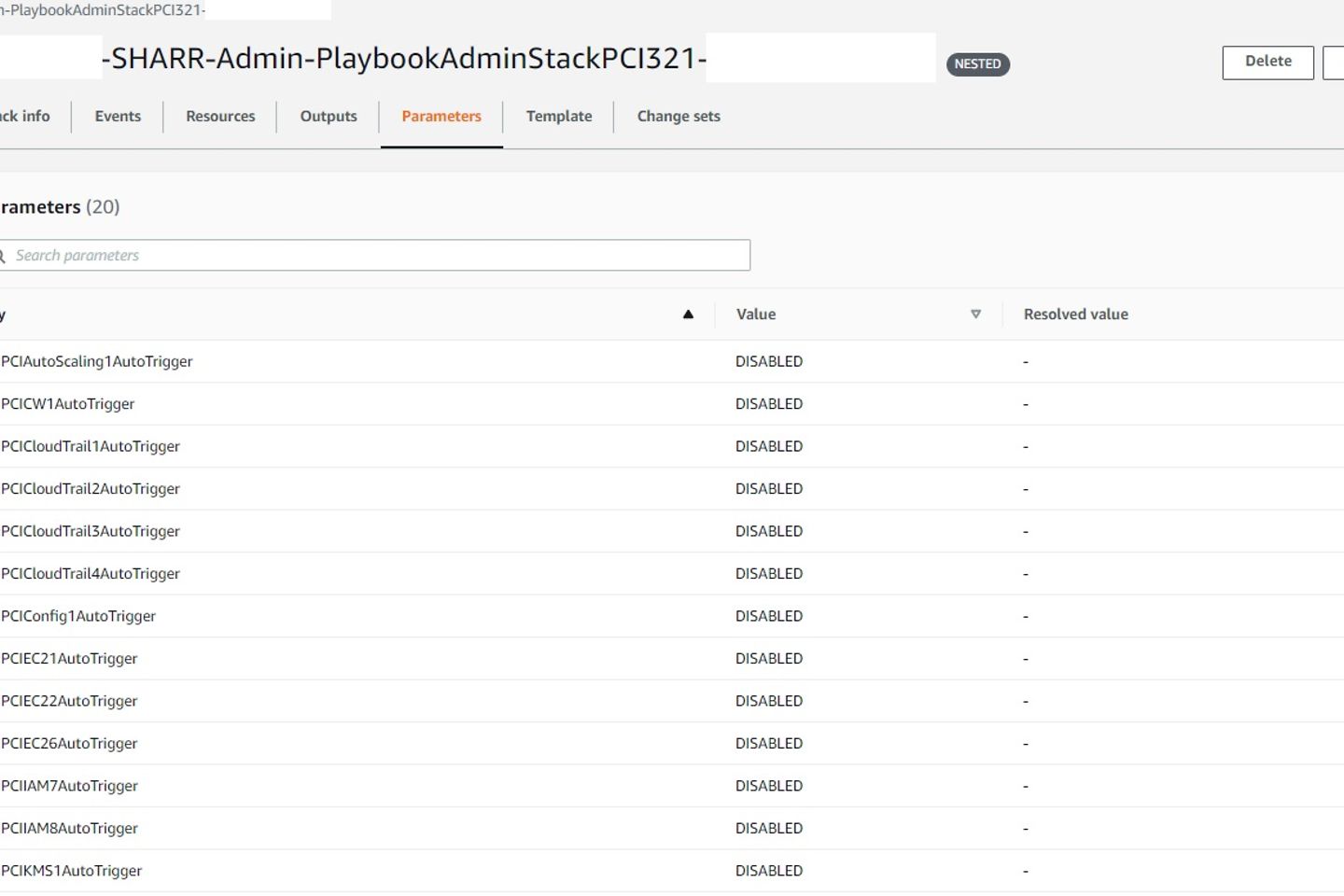
It is available as an AWS CloudFormation template. You can roll the solution out to any AWS environment with just a few clicks. It consists of the following:
Note: Since service-managed stack sets do not currently support nested stack sets, automation is needed to roll out the Member stack to new accounts. Depending on how you create your accounts, you should consider this as an additional step.
SHARR works in two ways: automated remediations and user-initiated remediations.
By default, all automated remediations are disabled. The parameter of the admin stack in the delegated Security Hub admin account needs to be updated to enable a specific automated remediation for all or some of the accounts in the AWS Organization.
As each security standard has distinct characteristics, a nested stack is created for each one activated. After activating the automated remediation, it gradually starts to fix all findings. This can take up to 24 hours in some cases, as the AWS Security Hub updates the compliance status of the individual findings every 24 hours.
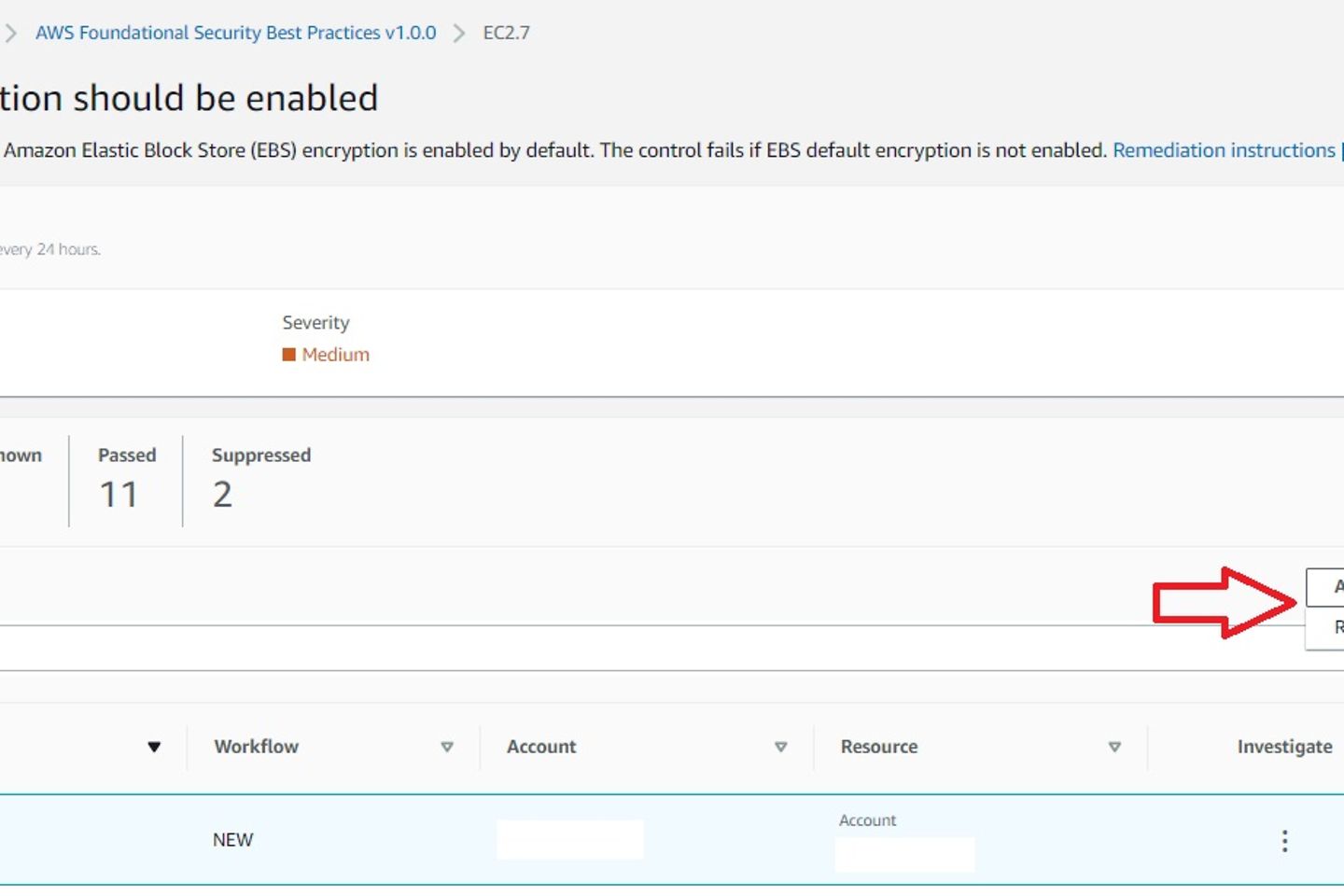
The Security Hub dashboard conveniently addresses the user-initiated remediations. An Amazon CloudWatch Event rule is invoked in the background, triggering the respective playbook automation.
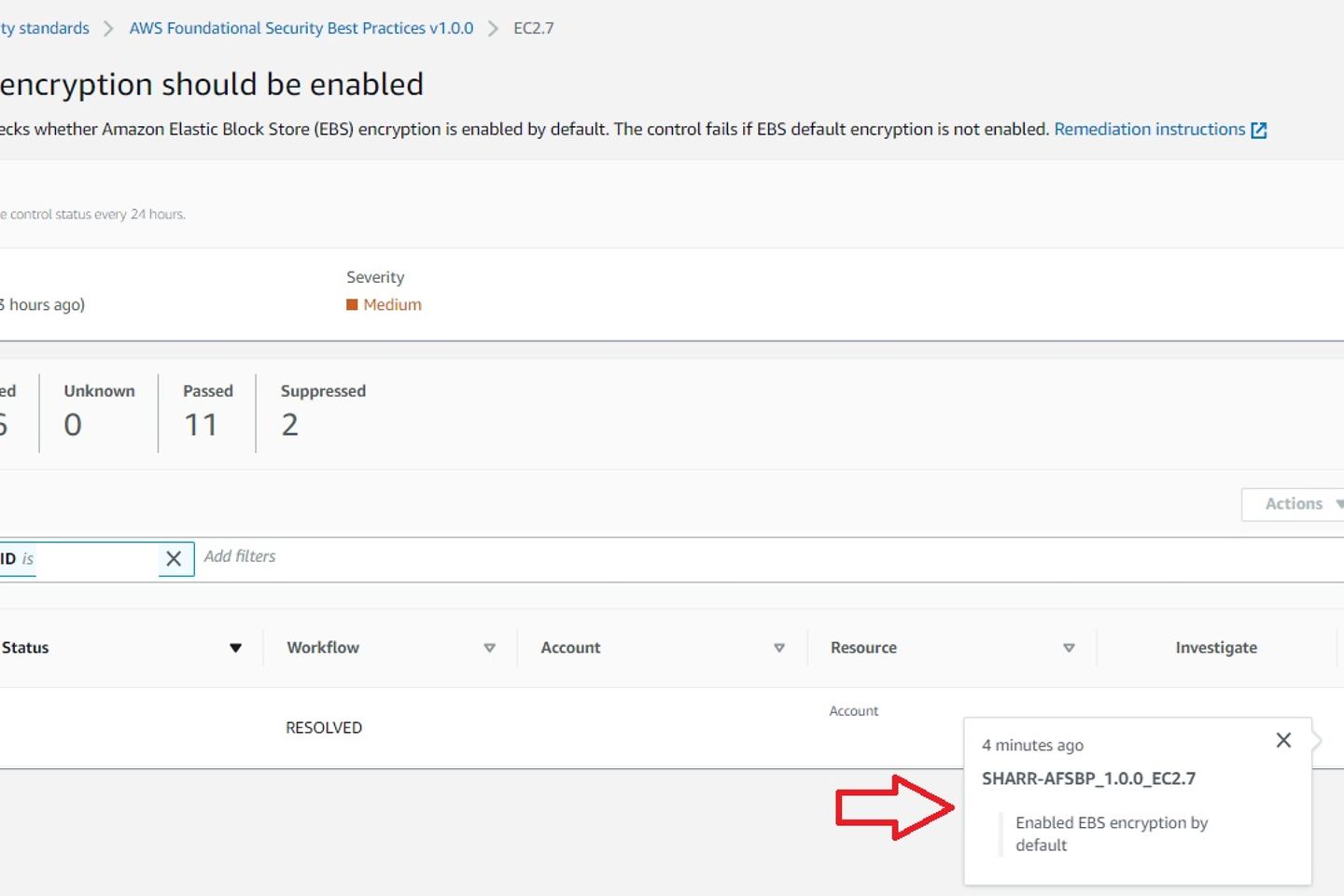
After the automation successfully resolved the finding, the workflow status updates to ‘resolved’, and an entry appears in the finding notes. Another 24 hours later, the compliance status automatically updates from ‘failed’ to ‘passed’.
AWS's Security Hub is not a set and forget solution. Responsible use and management of credentials, tracking current threats, and compliance with your company's policies are essential.
AWS offers SHARR as a foundation for automated security management of your AWS environment according to best practices.
Although there is not an automated remediation for every finding, the documentation on how to fix them manually is excellent. However, you also have to explore the available automated remediations and activate them one by one, where it applies to your environment. And hopefully, the automated remediations can be activated via the Security Hub dashboard sooner or later.