
In centuries past, building walls around a castle was one of the commonest ways to defend it. These walls had other elements, like towers, moats, and drawbridges. A conventional cyber security approach is very similar to this defense model, called the castle-and-moat model or perimeter-based security.
But nowadays, businesses must put equal effort into building both external and internal defenses. They can achieve this through microsegmentation.
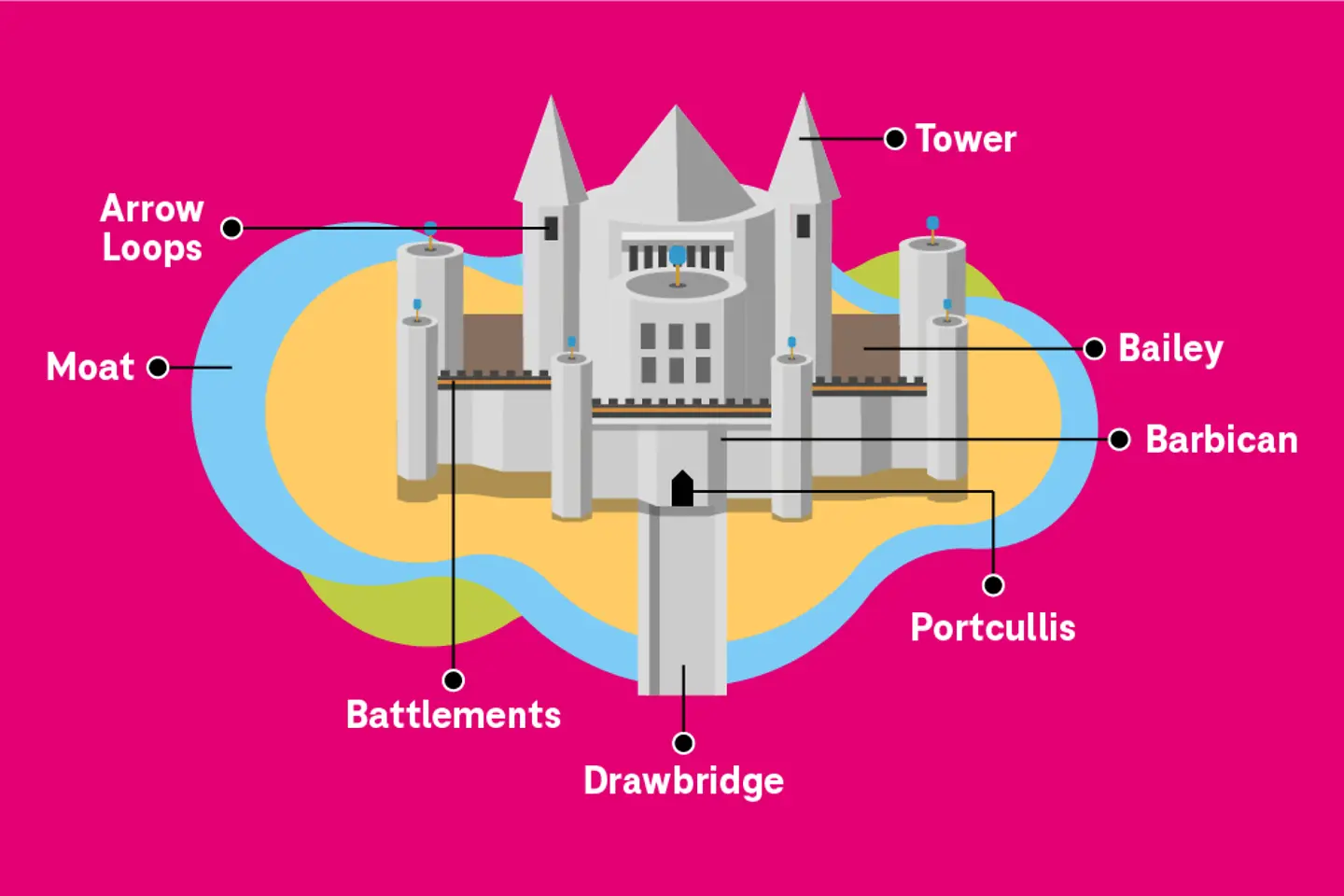
A conventional security model has some fundamental flaws; it automatically trusts everything inside the perimeter and assumes that attackers will not emerge from inside. Moreover, if the walls are breached, there’s nothing inside the castle to defend or contain attacks.
Malware and advanced persistent threats (APTs) linger to strike organizations. A traditional perimeter-focused security setup, therefore, is ineffective in today’s times. Despite different security systems like firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion preventions system, some cybercriminals may still be able to breach your perimeter. These threats can remain inside a company’s network in a sleep state network for months before becoming active. Nowadays, coordinated cyberattacks are notorious for lying undetected for weeks and months before full-fledged attacks.
These threats then leap in a lateral movement from server to server, enabling cybercriminals to exploit sensitive data as there are few security controls to contain the attack.
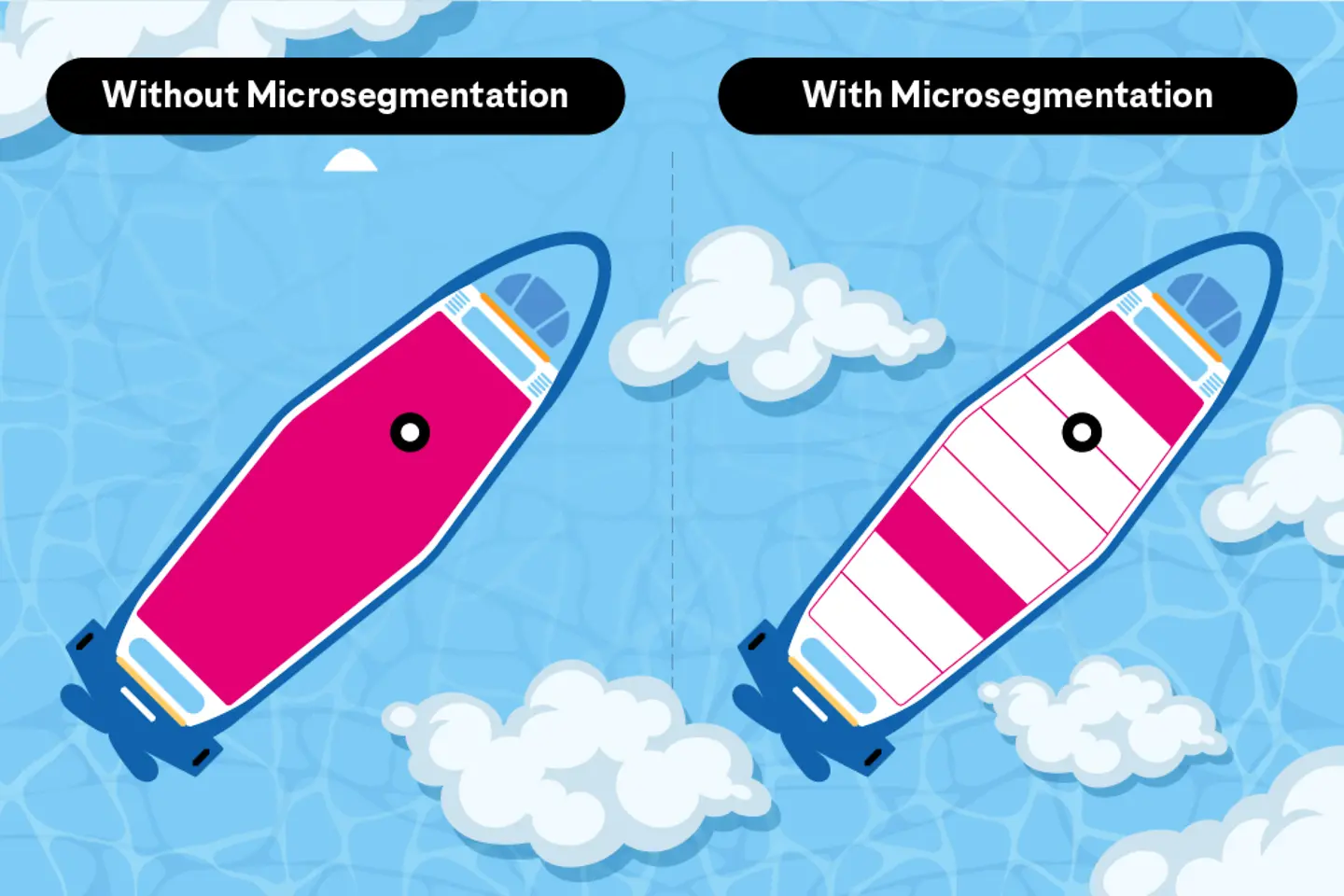
The main objective of microsegmentation is to restrict attackers’ movements inside a company’s systems to contain the damage to a large extent.
Network segmentation allows organizations to divide servers, systems, workloads, and applications into smaller isolated segments. Different segments can have unique security controls.
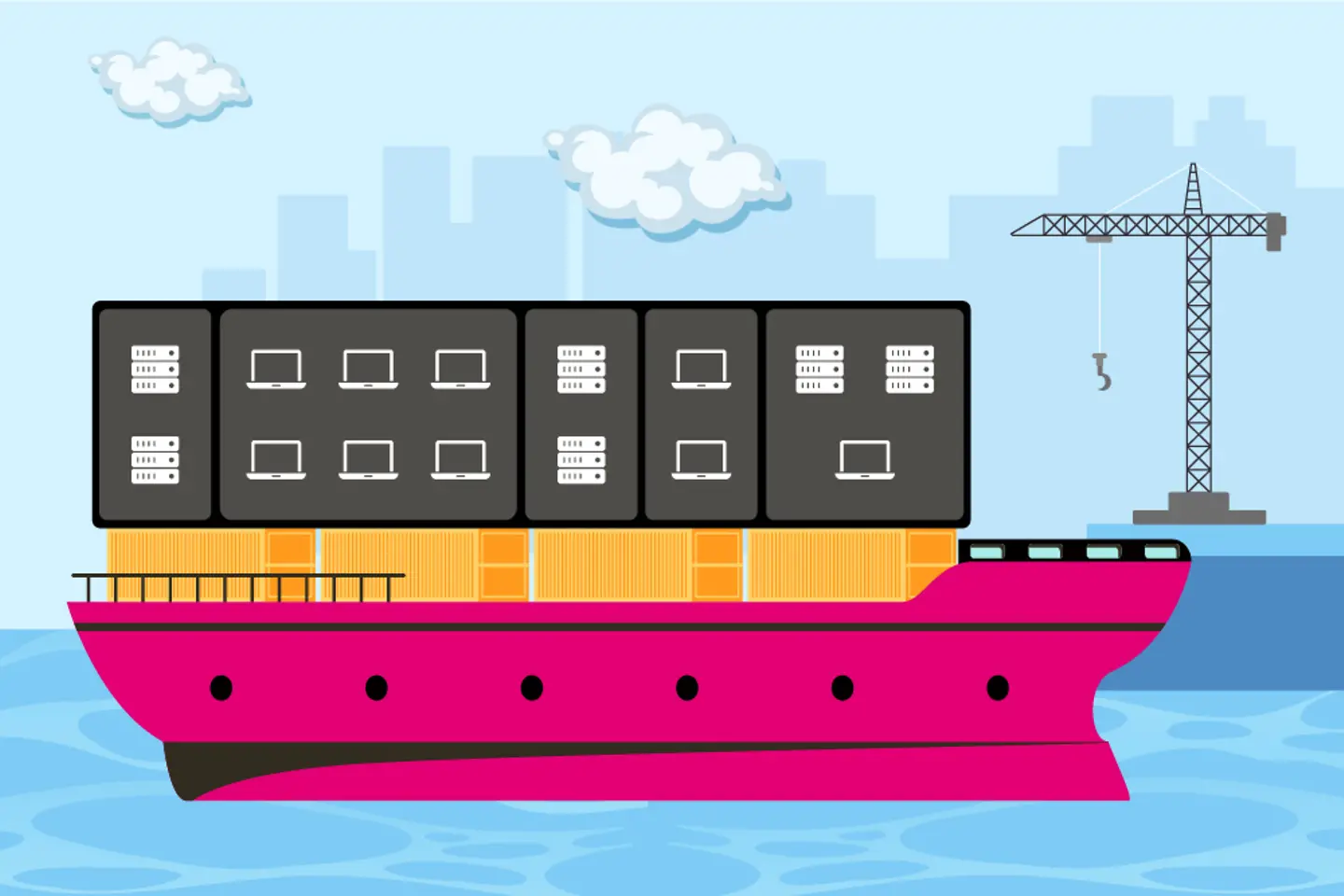

The concept is often compared to a submarine design, where the segments or compartments are built so that if there’s a breakage or puncture in one of the compartments, the flooding is contained to that section only. The other areas remain watertight.
The organization can contain the attack if a hacker intrudes in one of the segments. This restricts the malicious actor’s ability to move from one segment to another and allows organizations to minimize the attack surface. As the hacker remains locked inside one area, their visibility into others is also limited, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Enterprises can deploy different security control levels to reflect each segment’s criticality. Simply put, you can give your segments containing critical systems or sensitive data an extra layer of protection. Furthermore, these controls can trigger alarms in case of a breach related to that segment. Such features improve threat detection at early stages.
As more enterprises adopt cloud platforms, perimeter-based security becomes less relevant, and concepts like microsegmentation and zero-trust security are gaining ground. Micro-segmentation fits the bill for those with critical assets and infrastructure that need an extra layer of protection from ransomware and other cyber-attacks. The benefits include:
Maersk was one of the many companies severely impacted by the NotPetya ransomware attack.
The logistics giant was unknowingly using compromised accounting software, M.E.Doc. In June 2017, companies using the software received an update in a phishing email containing malware. The attack spread across networks like wildfire in under seven minutes, exploiting vulnerabilities. It also encrypted all the devices connected to those networks, rendering them unusable.
The attack struck Maersk like a bolt from the blue. As the world’s largest shipping company handling almost 1/5th of shipments, imagine the impact on world trade and logistics. The company was compelled to resort to manual operations during this time.
Interestingly, the company lost all domain controllers except one in Ghana. Due to a power cut, Ghana’s domain controller was off the network during the attack. This was a blessing in disguise; Maersk used that domain controller to restore its operations and recover data.
It was reported that the attack cost Maersk about US$ 300 million. Cumulatively, the NotPetya attack cost affected companies around US$ 1.2 billion.
Could Maersk have contained and mitigated the attack? It’s very likely.
Of course, it seems easy as we look in hindsight. Nevertheless, we must learn from others, especially in the cybersecurity domain. So, how should you approach microsegmentation?
Before implementation, we recommend considering the following:
T-Systems enables businesses to enforce process-level rules and policies to enhance their security posture. As a trusted partner of Akamai, T-Systems uses its Guardicore solution.
Whether your cloud environment is private, public, or hybrid, T-Systems can assist you in deploying microsegmentation. We can help you identify business-critical applications and create granular policies controlling the microsegments’ traffic flow.
You can even begin with our pre-defined templates and customize them to your needs.