
Flow logs do not capture all traffic flowing across the internet. If you need to monitor all IP traffic, including the payload, you can use AWS Fargate for traffic mirroring.

When monitoring devices or for out-of-band security, traffic mirroring is a technique for copying a specified ethernet interface’s incoming and outgoing traffic to a second interface for further analysis:
For analyzing traffic in AWS, the default option is to enable AWS VPC Flow Logs either by Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), subnetwork, or elastic network interface.
The flow logs capture the IP traffic flow, usually characterized by a Five-Tuple (or 5-tuple) set of values:
The main caveat of flow logs is that they do not capture all IP traffic. They do not log the following types:
Furthermore, flow logs only capture the traffic initiation itself. After establishing the session, the payload is not logged at all.
If you need to monitor all IP traffic, including the payload, consider using AWS’s VPC traffic mirroring.
Setting up the AWS VPC Traffic Mirroring architecture involves three steps. Firstly, you need to create a traffic mirror target that points to one of the following resources:
The easiest way is to spin up an AWS EC2 instance where an application is running, listening on the usual Traffic Mirror Port, which is 4789 UDP.
When creating the traffic mirror target, just select the network interface belonging to the pre-created EC2 instance.
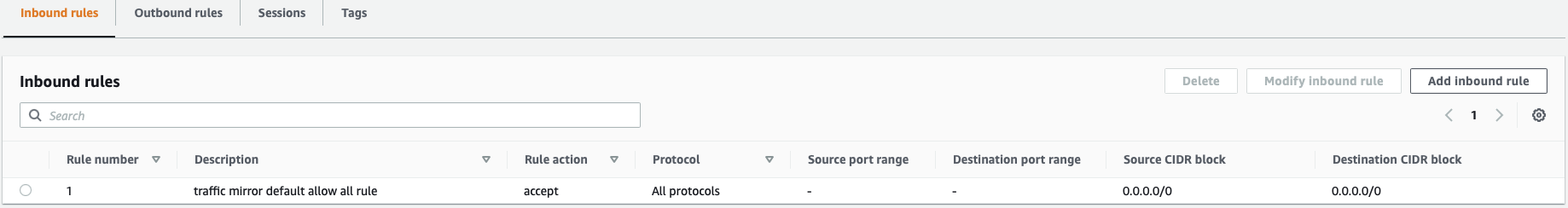
In the second step, create a traffic mirror filter which defines what kind of traffic you want to filter. You can limit the incoming data to a smaller subset by specifying one or more rules following the 5-tuple principle.
In our case, we created a rule as follows:
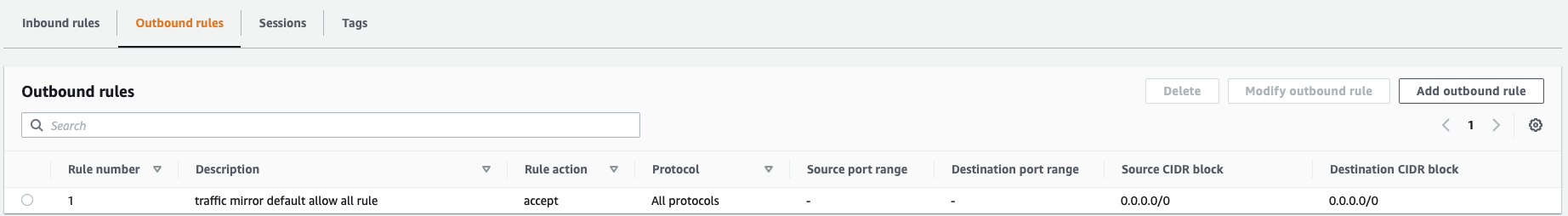
This rule just passes on every traffic to the configured traffic mirror target.
The third step is to create a traffic mirror Session. Select the source elastic network interface you want to track and point it to your previously created mirror target. Here, you also apply the filter we created in step two. In an ordinary non-autoscaling world, you are done with the setup, but because we are trying to log all traffic of an AWS Fargate service, the elastic network interfaces used are not static.
With every scaling event or redeployment, the interfaces will change, and the setup will need to be reconfigured.
As AWS Fargate services utilize the AWS Nitro System, all Fargate containers run on an elastic network interface, meaning they can mirror the traffic to the AWS VPC traffic mirror.
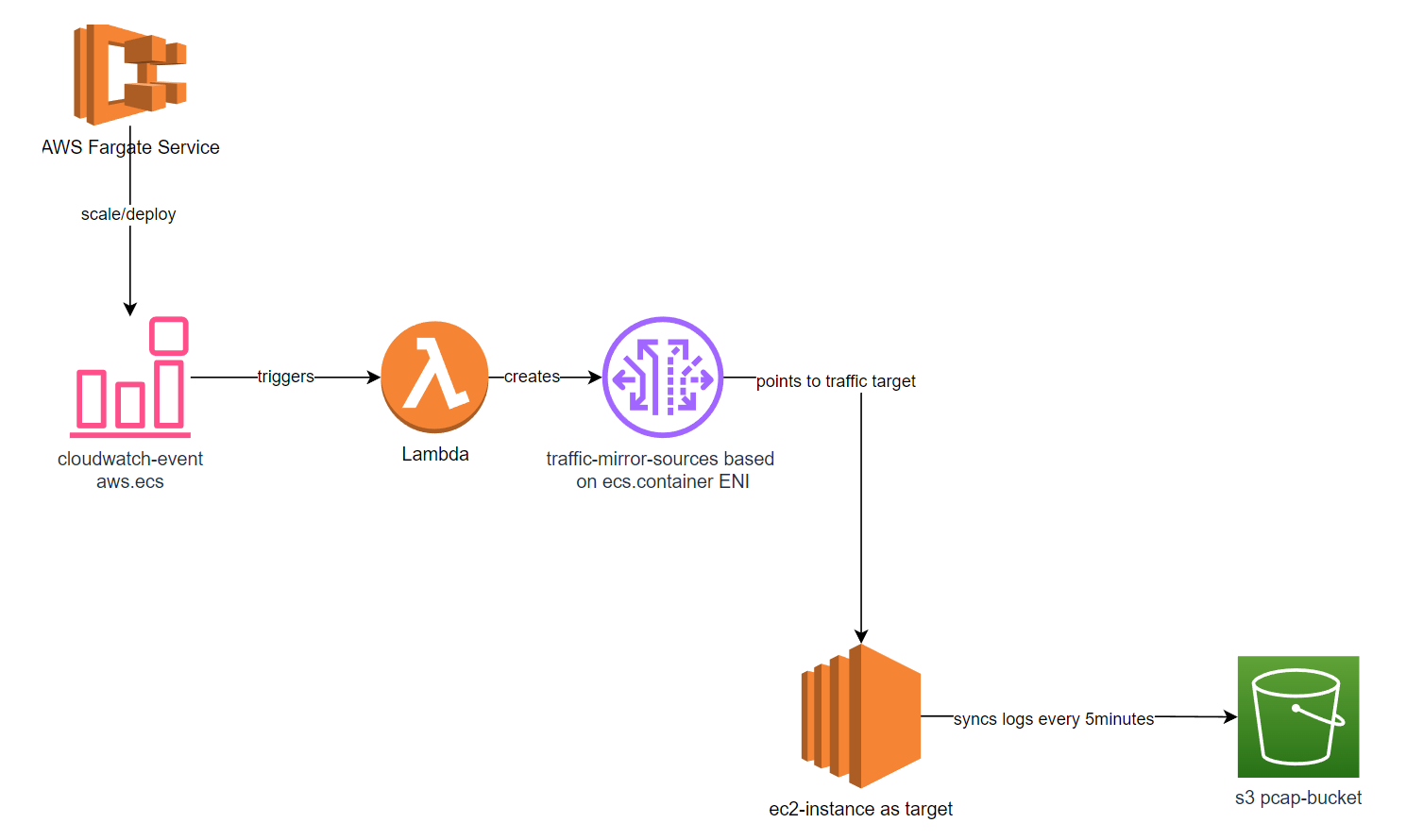
However, we also need to be notified about container service changes and respond to them. For this requirement, we can use the Amazon EventBridge combined with AWS Lambda. The architecture is as follows:
Click here to see an AWS Fargate use case.
This solution illustrates the essential components required to capture all traffic generated by an AWS Fargate service to an external traffic control system, such as Splunk, to conduct further traffic analytics.
Configuring the EC2 instance that receives the mirrored traffic is out of scope here but please contact us for more advice or a consultation.