
As healthcare accelerates its digital transformation, tech-driven trends are on the rise. A survey shows that nearly 70% of healthcare organizations are investing in digital platforms.1 This blog explores the surge in technology adoption from telemedicine and telehealth to electronic health records (EHR) systems. The blog highlights the growing security risks that these new changes pose.
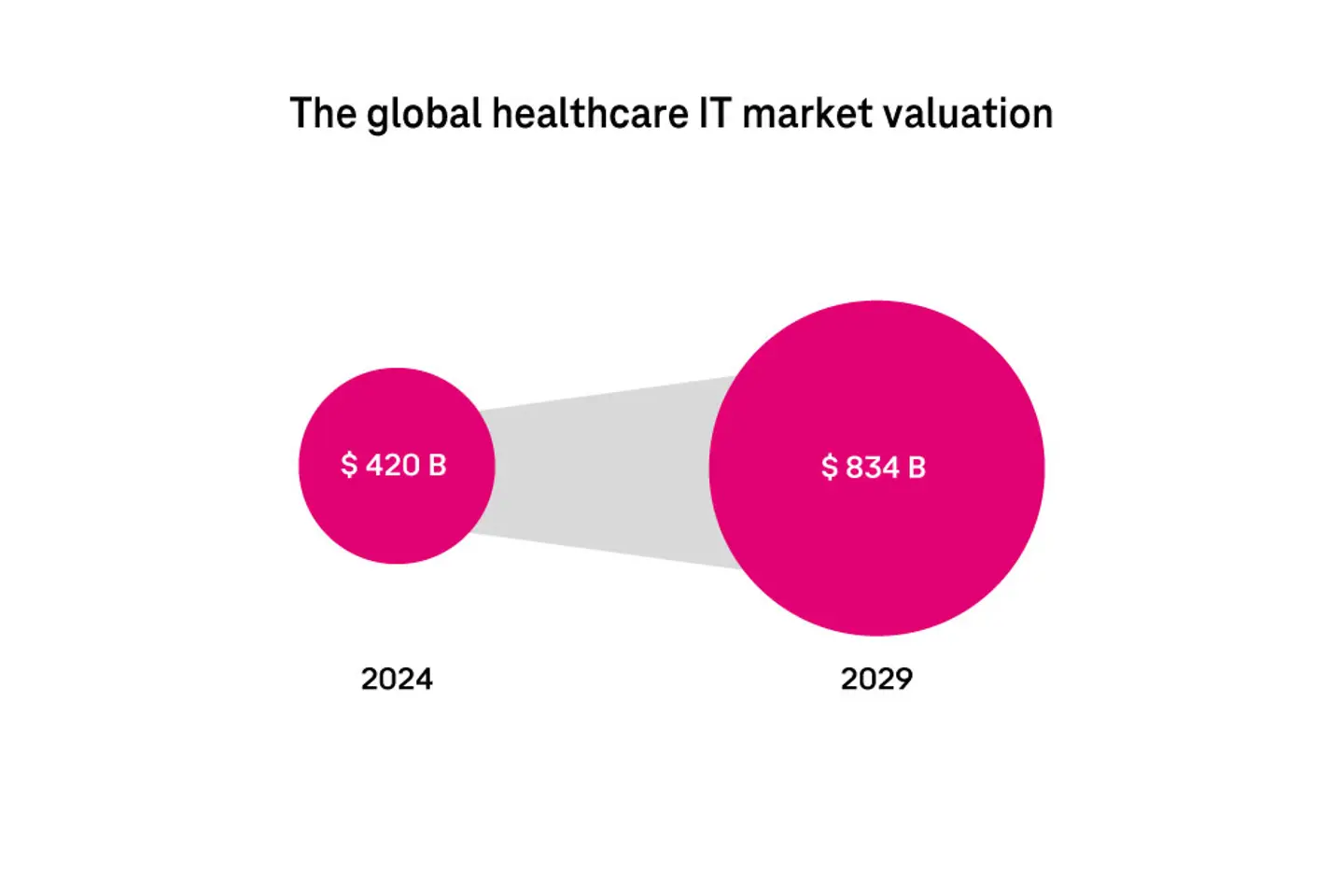
The top three trends impacting healthcare today are digital transformation, workforce (retention, well-being, shortage), and patient engagement (care and experience). In 2024, the global healthcare IT market was valued at over USD 420 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.7%, exceeding USD 834 billion by 2029.2 This rapid growth reflects the industry’s increasing reliance on technology to enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
Several factors are driving this growth. One major contributor is the burden of manual processes, causing hours of repetitive paperwork and data entry. On an average, healthcare providers spend around 15 hours per week on administrative tasks with specialties such as Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R) clocking up to 19 hours.3
This delays patient care and leads to staff burnout, further straining an already overextended and underpaid workforce.
In 2024, healthcare worker strikes surged globally, highlighting burnout and poor working conditions. Over 12,000 junior doctors in South Korea protested long hours and low staffing levels, with just 2.6 doctors per 1,000 people. In England, NHS junior doctors went on a prolonged strike, cancelling over 1.5 million appointments. New Zealand saw 36,000 nurses, midwives, and assistants strike for better pay and staffing.
Burnout from sustained stress continues to impact productivity, job satisfaction, and patient care. For instance, nurses spend about 15-28% of time on low-value tasks, while doctors spend about 70% of their time on admin-related tasks.4 With budget constraints, institutions cannot onboard more professionals.
Can technology change the current status quo? Yes, and some healthcare institutions are already adopting digital technologies as a multi-pronged approach to reduce workloads, improve patient care, and operational efficiencies.
With technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML)/deep learning (DL), automation, cloud, and data analytics, healthcare organizations can streamline processes and cut down on manual tasks. Routine activities such as scheduling, reminders, enquiries, and billing can be handled digitally, making documentation faster, more accurate, and efficient.
EHR systems are increasingly integrated with AI and ML to support diagnoses and improve care. These technologies are replacing outdated paper-based methods. Beyond productivity, automation reduces costs. For instance, North West London University Healthcare used UiPath to save over USD 461,000 annually and 56 hours daily by automating 18 processes.5
Trends such as EHR, telehealth, telemedicine, virtual assistants, diagnostics, EDI, e-prescription, and claims management are expanding. AI, ML, and DL could generate annual savings of USD 200–360 billion, according to McKinsey.6
The recent rise of generative AI (GenAI) is noteworthy in the healthcare industry with many organizations already using it for clinical decision-making, improving patient experience, and enhancing administrative efficiency. Philips Healthcare, for instance, is transforming its healthcare with GenAI and cloud capabilities. The company is implementing GenAI for automated document generation, scheduling, report generation, and so on. This initiative is expected to streamline admin operations, engage patients, and empower clinicians.7
It’s not just Philips, numerous healthcare providers are making significant IT investments. Over 40% have already experienced average to significant returns through GenAI investments.8 More than 85% of healthcare decision-makers are currently investing or planning to invest in GenAI in the coming three years.9
As IT becomes increasingly embedded into healthcare, it fuels a surge in data generation. The growing Internet connectivity of medical devices, driven by the rise of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), enables remote monitoring and more affordable care. IoMT is already a billion-dollar market due to its role in enhancing patient experience.
For decision-makers, medical data is a goldmine. Using descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, healthcare providers can extract critical insights and empower doctors with actionable information.
With such benefits, even several government bodies across the globe are pushing for reforms in the healthcare sector. For instance, the German government enacted several laws in the recent past to support the adoption of digital systems. In 2019, they introduced the Digital Care Act (DVG) to promote the use of electronic health records instead of paper-based documentation. Next, the Hospital Future Act (KHZG) was enacted to support hospitals in establishing IT infrastructure and strengthening cyber security through government funding. Under this initiative, the government allocated €4.3 billion in funding.10
Similar trends can also be seen in Asia where governments are pushing for data standardization and cloud-based electronic medical records (EMRs) to accelerate digital transformation. These initiatives aim to enhance interoperability, data sharing, and patient care through national digital health strategies.
Another phenomenon propelling digitalization is the industry's staff shortage. About 67% of healthcare CEOs feel that a shortage of skills will impact profitability over the next decade.11 This shortage can be dealt with by solutions such as agentic AI solutions that can complete complex tasks and meet objectives with minimal or no human supervision.
Unlike traditional chatbots, agentic AI increases staff productivity by automating multi-step processes across business functions. To address revenue challenges, reduce staff burnout, improve efficiencies, and enhance access, healthcare leaders are banking on digital technologies as outlined earlier.

As healthcare adopts more digital technologies such as the cloud, EHRs, and remote care, the attack surface expands. A typical hospital room has 20 IoMT devices, many with known vulnerabilities, and 82% of healthcare organizations faced at least one device-related attack in 2024.12
Third-party vendors also pose risks. In the past two years, 98% of organizations worked with a vendor that experienced a breach.13 Even basic collaboration tools are targets; 61% of professionals cited text messaging as the most attacked, followed by email.14
The average data breach cost in healthcare stands at USD 9.77 million (2024), which is the highest cost compared to other industries and almost double the average cost across all industries.15 Such extreme financial consequences can easily put smaller institutions out of business.
The data breaches in this industry are also expensive because regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST), Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2), and others levy heavy penalties for data breaches stemming from non-compliance. The cost of remediation is also high owing to the data complexity.
The healthcare industry is targeted the most because patient data (personal health information – PHI) holds significant value on the black market and the dark web. This patient data often includes personally identifiable information (PII), medical history, insurance information, payment details – all of which can be easily exploited.
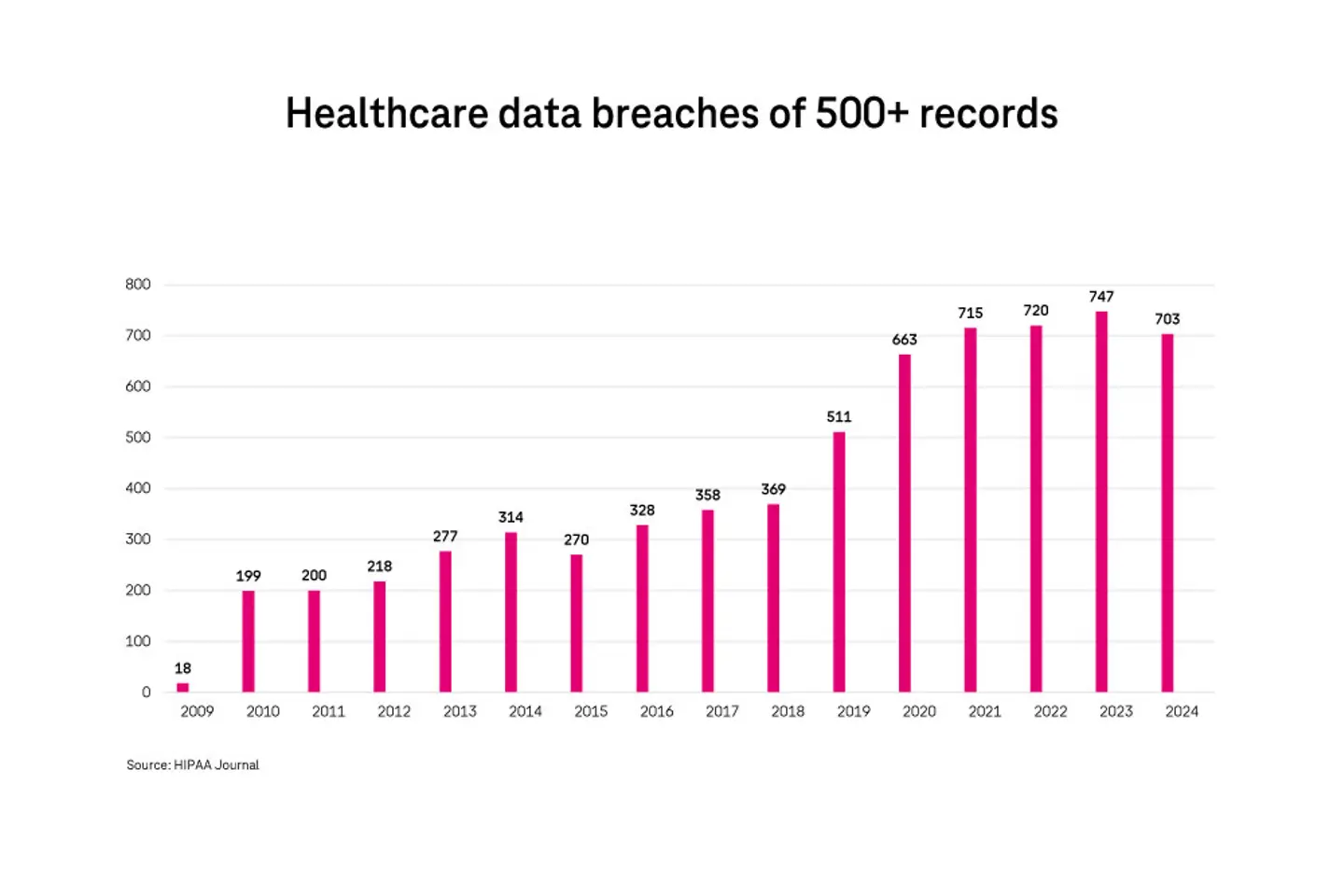
The graph shows the extent of security breaches in the industry. Although these numbers concern the USA alone, they’re indicative of the rising attacks and individuals being impacted by security risks each year.16
In over 70% of the cases, cyber attacks disrupt hospital and clinic operations preventing them from offering timely care to patients.17
Some attacks have forced hospitals to delay treatment, with serious consequences in critical cases. Common threats such as ransomware, business email compromise (BEC), supply chain, and cloud/account Compromise often cause treatment delays and operational complications. In the USA alone, about 168 million records were exposed due to data breaches in 2024.
The attack on Change Healthcare, a key player in healthcare technology and claims processing, reported a breach involving PHI due to a sophisticated ransomware attack. The company initially downplayed the impact to 500 individuals, but investigations discovered that approximately 100 million people were impacted, making it one of the largest healthcare data breaches in US history. The attack disrupted Change Healthcare's services and heightened concerns about patient data privacy and system reliability.
The financial impact of the breach was staggering. UnitedHealth Group, which had acquired Change Healthcare, incurred over USD 3.3 billion in expenses to compensate hospitals and healthcare providers for the disruptions caused. The breach prompted federal investigations into Change Healthcare's compliance with the HIPAA and raised alarms about the consolidation of private health data, further intensifying discussions around data security in the healthcare industry.
The breach highlighted the critical need for robust cyber security measures in healthcare infrastructure, spurring industry-wide discussions on adopting voluntary cyber security standards. While investigations and corrective actions are ongoing, the incident underscores the heightened risks of sophisticated cyber attacks targeting sensitive healthcare systems. The company is also said to have paid about USD 22 million in ransom (Bitcoins) to recover the data. This attack was orchestrated by the infamous hacker group BlackCat.18
An increasing number of healthcare organizations are realizing the impact of having security measures in place. About 78% organizations are planning to enhance security in 2025.19
Security solutions such as network segmentation, zero trust, extended detection and response, vulnerability management, and penetration testing, can help healthcare organizations improve their security posture, avoid cyber attacks, reduce data breach-related costs, and above all, ensure seamless patient care. Organizations with mature AI and automation processes reduce costs by USD 1.76 million while also lowering the time to detect attacks.20
T-Systems offers advanced security solutions for healthcare organizations that are AI-enabled to protect devices, data, networks, and overall IT infrastructure. With full-scale global security operations centers (SOC) and managed services, our threat detection capabilities respond to security incidents and thwart attacks in real time.
Our proactive approach ensures compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, HITRUST, NIS2, GDPR, and more while protecting sensitive patient data from breaches. With this level of security, healthcare organizations can focus on delivering care, while being confident that their systems and data are secure against modern cyber threats.
To find out how these security solutions work, and how you can protect your IT infrastructure, read our comprehensive white paper ‘Protecting patient safety through healthcare cyber security.’ Partner with us to secure your IT, OT, and networks. Strengthen your security and improve compliance. Start with a security assessment.
1 Global Healthcare Outlook Article, 2025, Deloitte
2 Healthcare Market Growth, 2024, MarketsandMarkets
3 Physician Statistics Article, 2024, Medscape Physician Compensation Report
4 Global Healthcare Outlook Article, 2025, Deloitte
5 Automation Case Study, 2024, UiPath
6 Digital Transformation and Health Investments, 2024, McKinsey
7 GenAI Philips Case Study, 2023, Philips Website
8 Global Healthcare Outlook Article, 2025, Deloitte
9 Future Health Index Report, 2024, Philips Website
10 German Digital Health News, 2021, Healthcare IT News
11 Healthcare Workforce, 2023, PwC
12 Healthcare Attack Surface Report, 2024, Praetorian
13 Healthcare Attack Surface Report, 2024, Praetorian
14 Cost and Impact of Patient Safety, 2024, Ponemon Institute
15 Cost of Data Breach Article, 2024, Security Intelligence
16 Data Breach Report, 2024, HIPAA Journal
17 Cost and Impact of Patient Safety, 2024, Ponemon Institute
18 Largest Healthcare Breaches, 2024, TechTarget
19 Global Healthcare Outlook Article, 2025, Deloitte
20 Cost of Data Breach Article, 2024, Security Intelligence